 |
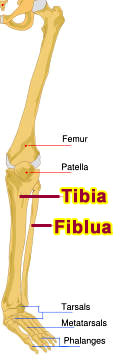
Fibula (Calf bone) and Tibia (Shinbone)
|
The fibula and tibia are the two bones in the lower leg. The fibula, or calf bone, is the smaller of the two and the most slender of the long bones, the bones of the arms and legs. The tibia, also called the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger and stronger of the two bones. It connects the knee with the ankle bones. When humans are born, they have epiphyseal plates, or growth plates, at the ends of certain bones such as the fibula and tibia. Throughout childhood, these plates expand causing the long bones to grow longer. By the time a person reaches his mid twenties, the plates have stopped growing. In addition, the deterioration of bone caused by diseases such as arthritis and osteoporosis is more often found in older people. By looking at the condition of these areas of the long bones, scientists can determine the approximate age of an individual. The length of the long bones can also be used to help estimate a personís height by comparing the measurements of the bones to other skeletons whose height is already known. |
 Compared to humans, we armadillos have short little legs. But we can still scurry around mighty fast and even jump three feet, straight up in the air! |
What can the fibula and tibia of our sailor tell us?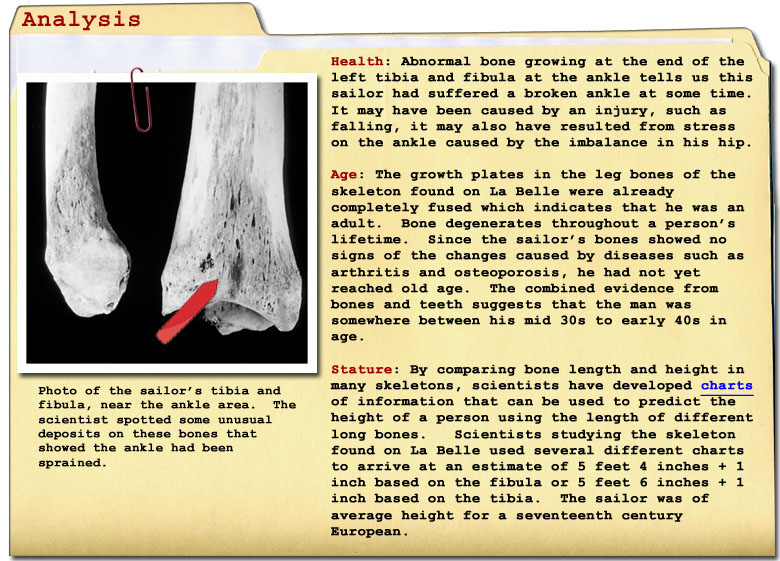
|